【译】FloodLight官网开发者文档五
Floodlight rest API开发
利用rest接口编写应用不限于编程语言,基本开发步骤如下: 1、确定应用所需的网络服务信息 2、从 Floodlight REST API列表中选择满足服务需求的REST API 若发现合适的接口,根据rest API语法,输入参数和必要的选型信息。 若没有现成的接口,相关服务和信息已能够有floodlight提供,但未封装为接口,则需自主开发相关接口。 若floodlight当前也不能实现相关服务,则需要基于Java自主开发控制器模块或应用模块 3、利用所有可以用的rest API调用,设计,实现,测试应用 在floodlight/apps 目录下,有一个用Python编写的Circuit Pusher应用实例,用于在同一openflow集群中的两个具有IP地址A和B的主机之间创建一个静态单路径链路。其开发过程按上述步骤执行。 1、确定应用所需的网络服务信息 主机A和B的接触点,即可表示主机物理位置的数据信息 主机A和B对应接触点之间的路由 用在A到B路由上所有交换机上部署流量信息服务
2、选择能够满足服务需求的REST API
/wm/device/ 发现每个设备的接触点信息
/wm/topology/route/
Floodlight-Test
Floodlight-Test是一个测试执行框架,与floodlight共同发布 ,供开发者实行floodlight一体化测试,以及各种扩展开发。 Floodlight-Test 允许如下开发:
- 实例化一个或多个有mininet的虚拟机
- 在开发者主机(如在Eclipse上)或虚拟机上运行floodlight
- 运行一组提供的一体化基础测试
- 为所有新扩展的部分添加新的一体化测试
Floodlight-Test用于保证floodlight和其所有扩展部分的高质量,Flood-Test支持并帮助开发者在他们设计的过程中遵守正确的测试原则,此外,它还是社区贡献给floodlight资源库的质量标准。 起初,Floodlight作为一个开源控制器,去建立openflow应用和/或控制特征。后来,在开源社区的贡献下成长为一个平稳的控制平台。Openbench将会提供测试工具和过程保证floodlight的健全成长。 系统需求 1 VirtualBox v4.1.14 或更新(较新的版本可能有效但是未测试过 ) 2 开始安装时网络连通性 3 Floodlight vmdk 安装步骤 1.在主机中,下载 floodlight-vm.zip, http://www.projectfloodlight.org/download/;解压到你指定的工作目录 , say ~/work
-
在主机中,获取VM安装脚本:
$git clone https://github.com/floodlight/floodlight-test scripts are under floodlight-test/scripts
3.两种方案: a: 重命名VM压缩文件,改为onetime-create-vm.sh 中给定 的默认名(如 floodlightcontroller-test); b:编译 onetime-create-vm.sh 中的文件名,与VM文件相匹配 (如., floodlightcontroller-[release date]).
- 在主机中, 运行 onetime-create-vm.sh; 在 VirtualBox 图形界面上, 点击 “Network” 和 “OK”,然后点击启动虚拟机, 登录 (username: floodlight, no password), 运行 ‘ifconfig’ 确认并记录eth0的IP地址。
- 在主机中, 用VM IP编译onetime-setup-vm.sh和setup-bench.sh ; 运行onetime-setup-vm.sh ,将会进入VM (consolve-vm) 并且安装Floodlight-Test 。
运行测试 每次你想进行测试,你需要打开所有虚拟机并且做如下步骤:
- 如果需要则更新 floodlight.jar (以及 floodlight.properties) : 倘若你还未改变 floodlight 代码 (i.e., floodlight.jar is up-to-date on your test VMs),你可以简单的打开这三个 虚拟机(一个控制机,两个测试机) 如果你需要更新 floodlight.jar, 提供一个简便的方法,在update-floodlight.sh中更新路径为floodlight源文件根目录;更新VM IP ;运行update-floodlight.sh 。
- 在 “console” VM, ‘cd floodlight-test’ 然后 ‘source setup-python-env.sh’
- 在 “console” VM, ‘bm clean’ ,清空之前运行时旧的VM状态.
- Edit build/Makefile.workspace to confirm/edit VM IP addresses under make target ‘register-vms-floodlight’
- 在 “console” VM, ‘bm register-vms-floodlight’
- 在 “console” VM, ‘bm check-vms-floodlight’; see failed-check-vms-floodlight file for failed tests, if any
- 在”console” VM, ‘bm check-tests-floodlight’; see failed-check-tests file for failed tests, if any 8.在 “console” VM, ‘bigtest/[test-dir]/[test.py]’ to run individual failed tests directly to diagnose cause of failure 有效建议: 1.一开始安装就为 “tester VMs” 拍快照 ,点击一个VM, 点击右上端的Snapshots然后点击“add ”添加快照。例如,运行完 check-tests-floodlight 后你想恢复 画面到默认模式。 2.使用ssh客户端可以查看更多历史
- 很多安装错误都是由于网络错误,如以下典型错误:
- 在网桥模式下配置安装脚本: ifconfig 确保拥有有效地址,若没有,可以在DHCP服务器中 设置IP,也可以 点击 VirtualBox VM’s GUI Network tab,若都不行,分配静态IP,’ifconfig eth0 xx.xx.xx.xx 255.255.255.0’
- 安装后,VirtualBox menu bar > VirtualBox > Preferences > Network > Add a host-only Network,如果没有 (vboxnet0). 点击VM’s Network,设置为host-only Adapter/vboxnet0.
合并floodlight扩展部分的要求 Floodlight 严格执行质保联系,floodlight中所有模块既要单独测试又要整体测试.。
- JUnit unit tests. Code coverage threshold, eclipse, bm check
- OpenBench integration tests
- Floodlight committer tests and code review
添加新的一体化测试 用Python添加一个一体化测试的过程很明确,怎样创建测试环境,怎样快速添加自己的测试命令。 思考下面的例子:
-
bigtest/firewall/FloodlightFirewallTest.py#!/usr/bin/env python ## Creates a tree,4 topology to test different firewall rules ## with ping and iperf (TCP/UDP, differed ports) ## @author KC Wang # import a number of basic bigtest libraries import bigtest.controller import bigtest # import a number of useful python utilities. # This particular example does REST API based testing, hence urllib is useful for sending REST commands and # json is used for parsing responses import json import urllib import time from util import * import httplib # bigtest function to connect to two active tester VMs # make sure you already started the VM and have done bm register-vms-floodlight # (with the correct two nodes indicated in build/Makefile.workspace) env = bigtest.controller.TwoNodeTest() log = bigtest.log.info # use the first tester VM’s floodlight controller # since its a linux node, we use its bash mode as command line interface controllerNode = env.node1() controllerCli = controllerNode.cli() controllerIp = controllerNode.ipAddress() controllerCli.gotoBashMode() controllerCli.runCmd(“uptime”) # use the second tester VM to run mininet mininetNode = env.node2() mininetCli = mininetNode.cli() # this starts mininet from linux console and enters mininet’s command line interface mininetCli.gotoMininetMode(“–controller=remote –ip=%s –mac –topo=tree,4” % controllerIp) # this function uses REST interface to keep on querying floodlight until the specified switches are all # connected to the controller correctly and seeing each other in the same connected cluster switches = [“00:00:00:00:00:00:00:1%c” % x for x in [‘1’, ‘2’, ‘3’, ‘4’, ‘5’, ‘6’, ‘7’, ‘8’, ‘9’, ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’, ‘e’, ‘f’]] controllerNode.waitForSwitchCluster(switches)
现在你已经添加了一些用于不同情况的测试命令,确保floodlight正常工作。
....
# issuing a mininet command
# pingall should succeed since firewall disabled
x = mininetCli.runCmd("pingall")
# return is stored in x and the bigtest.Assert method can check for a specific string in the response
bigtest.Assert("Results: 0%" in x)
# you can use python's sleep to time out previous flows in switches
time.sleep(5)
# Sending a REST API command
command = "http://%s:8080/wm/firewall/module/enable/json" % controllerIp
x = urllib.urlopen(command).read()
bigtest.Assert("running" in x)
...
# clean up all rules - testing delete rule
# first, retrieve all rule ids from GET rules
command = "http://%s:8080/wm/firewall/rules/json" % controllerIp
x = urllib.urlopen(command).read()
parsedResult = json.loads(x)
for i in range(len(parsedResult)):
# example sending a REST DELETE command. Post can be used as well.
params = "{\"ruleid\":\"%s\"}" % parsedResult[i]['ruleid']
command = "/wm/firewall/rules/json"
url = "%s:8080" % controllerIp
connection = httplib.HTTPConnection(url)
connection.request("DELETE", command, params)
x = connection.getresponse().read()
bigtest.Assert("Rule deleted" in x)
...
# iperf TCP works, UDP doesn't
mininetCli.runCmd("h3 iperf -s &")
x = mininetCli.runCmd("h7 iperf -c h3 -t 2")
# bigtest.Assert can also test for a "not" case
bigtest.Assert(not "connect failed" in x)
-
bigtest/forwarding/IslandTest1.py这个例子展示怎样定义随机的拓扑结构,主机互联,交换机可按选择被不同控制器侦听。这在 OF岛与non-OF岛互联的拓扑中有用,因为控制器B控制的岛在控制器A看来是non-OF的。import bigtest from mininet.net import Mininet from mininet.node import UserSwitch, RemoteController from mininet.cli import CLI from mininet.log import setLogLevel import bigtest.controller from bigtest.util.context import NetContext, EnvContext def addHost(net, N): name= ‘h%d’ % N ip = ‘10.0.0.%d’ % N return net.addHost(name, ip=ip) def MultiControllerNet(c1ip, c2ip): “Create a network with multiple controllers.” net = Mininet(controller=RemoteController, switch=UserSwitch) print “Creating controllers” c1 = net.addController(name = ‘RemoteFloodlight1’, controller = RemoteController, defaultIP=c1ip) c2 = net.addController(name = ‘RemoteFloodlight2’, controller = RemoteController, defaultIP=c2ip) print “* Creating switches” s1 = net.addSwitch( ‘s1’ ) s2 = net.addSwitch( ‘s2’ ) s3 = net.addSwitch( ‘s3’ ) s4 = net.addSwitch( ‘s4’ ) print “* Creating hosts” hosts1 = [ addHost( net, n ) for n in 3, 4 ] hosts2 = [ addHost( net, n ) for n in 5, 6 ] hosts3 = [ addHost( net, n ) for n in 7, 8 ] hosts4 = [ addHost( net, n ) for n in 9, 10 ] print “* Creating links” for h in hosts1: s1.linkTo( h ) for h in hosts2: s2.linkTo( h ) for h in hosts3: s3.linkTo( h ) for h in hosts4: s4.linkTo( h ) s1.linkTo( s2 ) s2.linkTo( s3 ) s4.linkTo( s2 ) print “* Building network” net.build() # In theory this doesn’t do anything c1.start() c2.start() #print “*** Starting Switches” s1.start( [c1] ) s2.start( [c2] ) s3.start( [c1] ) s4.start( [c1] ) return net with EnvContext(bigtest.controller.TwoNodeTest()) as env: log = bigtest.log.info controller1 = env.node1() cli1 = controller1.cli() controller2 = env.node2() cli2 = controller2.cli() print “ip1:%s ip2:%s” % (controller1.ipAddress(), controller2.ipAddress()) with NetContext(MultiControllerNet(controller1.ipAddress(), controller2.ipAddress())) as net: sleep(20) ## net.pingAll() returns percentage drop so the bigtest.Assert(is to make sure 0% dropped) o = net.pingAll() bigtest.Assert(o == 0)
Unit测试
简介 Floodlight 采用 Junit 框架和 EasyMock进行单元测试。你可以运行所有Junit测试并且用ant检查单元测试的范围,命令如下:
# runs the unit tests with coverage
ant coverage
browse unit test reports at floodlight/target/coverage/index.html
开发新代码就得添加相应的单元测试,如果代码中涉及已存在的类,即使没有改变类,需要为这个类扩大单元测试范围。
例子 仔细阅读已有的单元测试,可以从net.floodlightcontroller.forwarding/ForwardingTest.java 或者net.floodlightcontroller.devicemanager.internal/DeviceManagerImplTest.java开始 写一个 EasyMock测试: 1.清楚要 “mocking” 什么,要测试什么; 记住你要测试的仅仅是代码,代码可能调用其他类的方法,但这是是那个类需要“mocked”的。 在ForwardingTest.java,在 src/test/java/.test packages中可以找到很多“mock class” ,当你需要模拟典型的floodlight服务时需要依靠这些类。同时会多次调用 createMock(.class) ,这是模拟类示例的基本组成。如果不知道选择哪种方法就参考已有的。
- 使用模拟接口方法就得进行声明,浏览代码记录下什么时候调用什么方法,打算用什么数测试,算出应该返回的正确结果。这些值应该包括正常情况以及边界情况,并且可以进行多个分开的单元测试,每次测试某一组值。
- createMock(), reset(), expect(), replay(), verify() 总而言之,用先用createMock()创建模拟对象,再用reset()清空对模拟对象的期望,之后用replay()进入准备状态,准备运行要被测试的代码,最后用verify()验证调用的方法使用情况是否与预期结果一致。任何一点不符都会出错。 4.测试范围 ‘ant coverage’分析了部分代码,即使是测试结果是100%也不代表代码完全正确。正确性取决于测试案例的范围,用常见值与边界值测试代码各种情况。 关于Junit 和EasyMock的阅读 Junit Tutorial (1) Junit Tutorial (2) Unit testing with JUnit and EasyMock Mock controls with EasyMock Using captures with EasyMock EasyMock README
控制器基准配置
基准配置
更新 floodlight properties文件
编译 src/main/resources/floodlightdefault.properties如下:
floodlight.modules = net.floodlightcontroller.learningswitch.LearningSwitch,net.floodlightcontroller.counter.NullCounterStore,net.floodlightcontroller.perfmon.NullPktInProcessingTime
创建 Floodlight Floodlight propertie文件缓存在 Floodlight jar.中,可以解压Floodlight 活着在 floodlight.sh根目录中添加以下命令 “-cf floodlightdefault.properties”
$ ant
运行 Floodlight 运行 floodlight.sh 。 注意 根据MAC地址的数量进一步调整内存性能。
Cbench (New) 用来测试openflow控制器。Cbench可以仿真一组连接控制器的交换机,发送packet-in消息,可用于测试细微变化产生的影响。 安装cbench 参考 http://www.openflow.org/wk/images/3/3e/Manual.pdf Chapter 2 中详细的安装指导。 Under debian/ubuntu Linux:
$ sudo apt-get install autoconf automake libtool libsnmp-dev libpcap-dev
$ git clone git://gitosis.stanford.edu/oflops.git
$ cd oflops; git submodule init && git submodule update
$ git clone git://gitosis.stanford.edu/openflow.git
$ cd openflow; git checkout -b release/1.0.0 remotes/origin/release/1.0.0
$ wget http://hyperrealm.com/libconfig/libconfig-1.4.9.tar.gz
$ tar -xvzf libconfig-1.4.9.tar.gz
$ cd libconfig-1.4.9
$ ./configure
$ sudo make && sudo make install
$ cd ../../netfpga-packet-generator-c-library/
$ sudo ./autogen.sh && sudo ./configure && sudo make
$ cd ..
$ sh ./boot.sh ; ./configure --with-openflow-src-dir=<absolute path to openflow branch>; make
$ sudo make install
$ cd cbench
此时可运行cbench
运行 cbench
Cbench 有一系列参数. 我们所需的有:

例子:
./cbench -c localhost -p 6633 -m 10000 -l 10 -s 16 -M 1000 -t
怎样用floodlight满足服务质量
简介 l Openflow1.0协议中有设置网络服务类型的方法,就像匹配流的包在某个端口进入某个队列。给使用者提供简单的方法将Qos状态压入交换机。协议1.3将进一步改进, 依旧支持DSCP 或ToS位,并构建深层次的Qos框架,OFconfig还是有重要作用,这样的协议对Qos队列的建立和拆除很有用。 l 以下示例就是将限速Qos状态压入OVswitches中 .https://groups.google.com/a/openflowhub.org/forum/#!msg/floodlight-dev/y5yJRTcfS48/418QH9zLMKoJ|https://groups.google.com/a/openflowhub.org/forum/#!msg/floodlight-dev/y5yJRTcfS48/418QH9zLMKoJ
QoS 应用
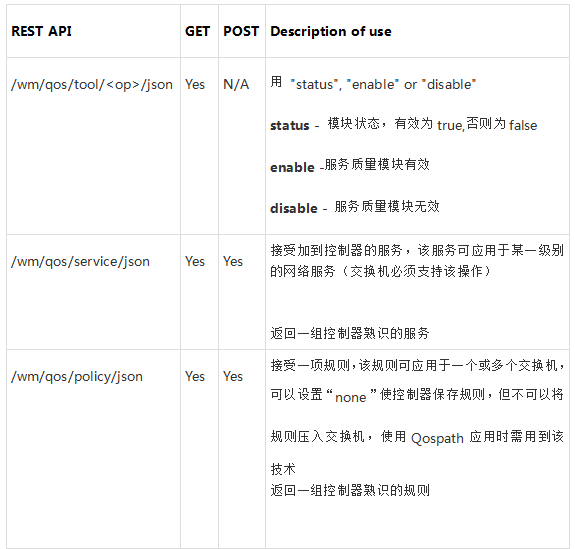
服务

规则
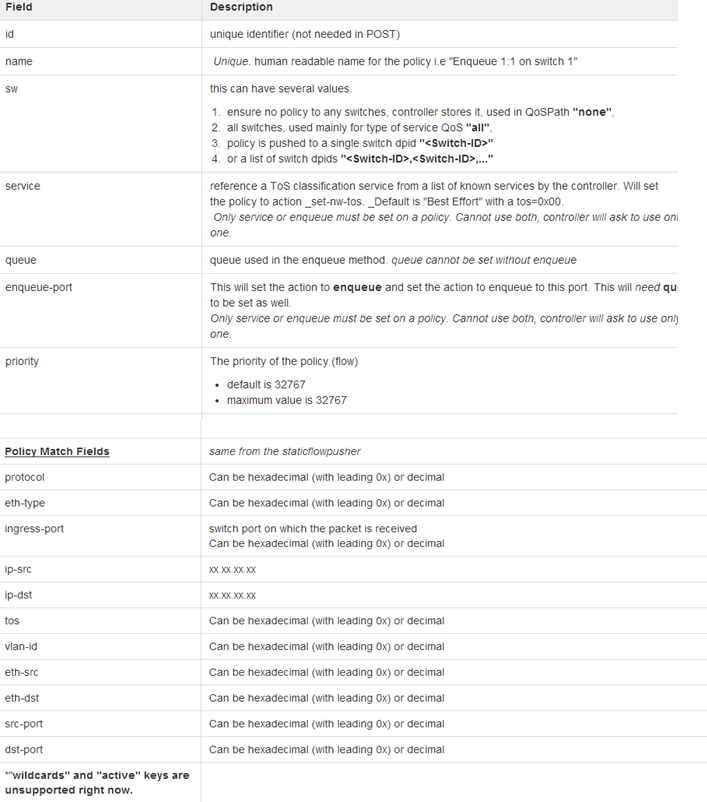
REST 应用 QoSPusher.py Python应用用来管理 QoS QoSPath.py QoSPath是一个python应用,用 cirtcuitpusher.py将 QoS 状态压入某网络的环路。 例子 Network
Mininet Topo Used
#sudo mn --topo linear,4 --switch ovsk --controller=remote,ip= --ipbase=10.0.0.0/8
最新评论